by Nitin Jain – Principal Consultant
Unless you’ve been living off-grid for the past few weeks, you’ve probably noticed that the internet is abuzz with excitement about ChatGPT. ChatGPT (short for Generative Pre-training Transformer) is an increasingly popular text-based AI (Artificial Intelligence) chatbot that delivers a written, formulated response based on a prompt given to it by humans. ChatGPT enables users to ask questions or tell a story and responds with relevant, natural-sounding answers and topics. The interface is designed to simulate a human conversation, creating natural engagement with the bot. Responses from ChatGPT sound quite human-like because they were trained on vast amounts of data written by people. ChatGPT is smarter than the auto-complete that we have today in email or messenger tools (like Teams), but it’s the same principle: it’s guessing what someone might plausibly say on a certain topic. Let’s dig-in a little further about ChatGPT.
Who Created ChatGPT?
OpenAI, a San Francisco-based AI and research company, launched ChatGPT (4.0) on November 30, 2022. OpenAI also created Whisper, an automatic speech recognition system, and DALLE•2, a popular AI image and art generator.
How Can You Use ChatGPT?
ChatGPT can be used for a variety of applications, including customer service, online shopping, hiring and training staff, streamlining operations, and providing more personalized customer experiences. ChatGPT can also be used to create interactive storytelling experiences, allowing users to explore and learn from virtual worlds.
Is ChatGPT Free to use?
The use of ChatGPT is currently free during the “research preview” time. The chatbot is currently open for users to try out and provide feedback on the responses so that the AI can become better at answering questions and learn from its mistakes. ChatGPT can be accessed via the URL – https://chat.openai.com/auth/login. One would need to register in order to be able to access it.
How Was ChatGPT Trained?
ChatGPT is a Large Language Model (LLM). There are many LLMs in the market like Turing NLG (from Microsoft), Bard/LaMDA (from Google), GPT-3 (from OpenAI), etc. Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained with massive amounts of data to accurately predict what word comes next in a sentence. LLMs predict the next word in a series of words in a sentence and the next sentences – kind of like autocomplete, but at a mind-bending scale. This ability allows it to write paragraphs and pages of content. But LLMs are limited in that they don’t always understand exactly what we as humans want. And that’s where ChatGPT improves on state-of-the-art, with Reinforcement Learning with Human Feedback (RLHF) training. ChatGPT RLHF as an additional layer of training that uses human feedback to help ChatGPT learn the ability to follow directions and generate responses that are satisfactory to humans. Training the LLM this way is revolutionary because it goes beyond simply training the LLM to predict the next word. What sets ChatGPT apart from a simple chatbot is that it was specifically trained to understand the human intent in a question and provide helpful, truthful, and harmless answers. Because of that training, ChatGPT may challenge certain questions and discard parts of the question that don’t make sense.
What are some of the use cases for ChatGPT:
- Generating responses in a chatbot or virtual assistant, to provide more natural and engaging interactions with users (conversational AI).
- Using chatbot-generated answers to create automated customer service tools for some of the repeating tasks.
- Creating personalized communication, such as email responses or product recommendations.
- Possible knowledge repository for personalized feedback.
- Foster ideas and expand human thinking abilities and promote creativity.
- Creating marketing content like blog posts or social media updates.
- To generate a shorter summary by recapping long documents by providing the full text.
ChatGPT can be useful for an Oracle DBA in several ways, such as:
- Automating repetitive tasks such as generating SQL scripts, reports, and monitoring metrics.
- Providing quick answers to common database questions, such as troubleshooting errors and performance issues.
- Generating documentation and tutorials for database management and administration.
- Simulating and testing different scenarios to make better decisions and plan for future changes to the database.
- Tuning SQL queries and improving performance.
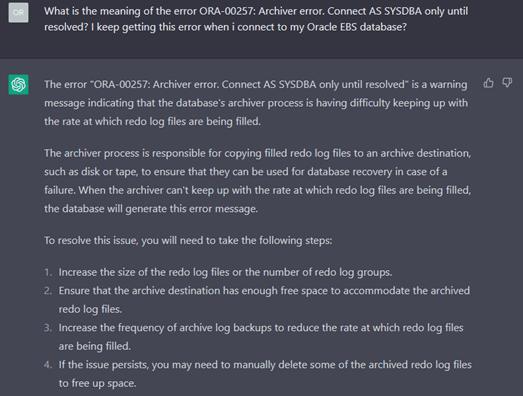
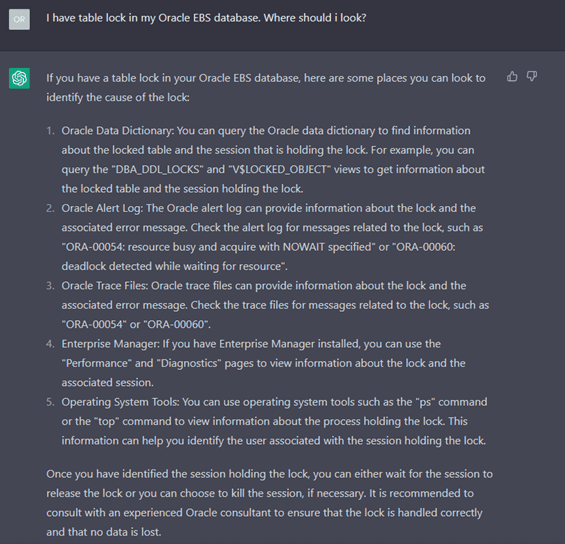
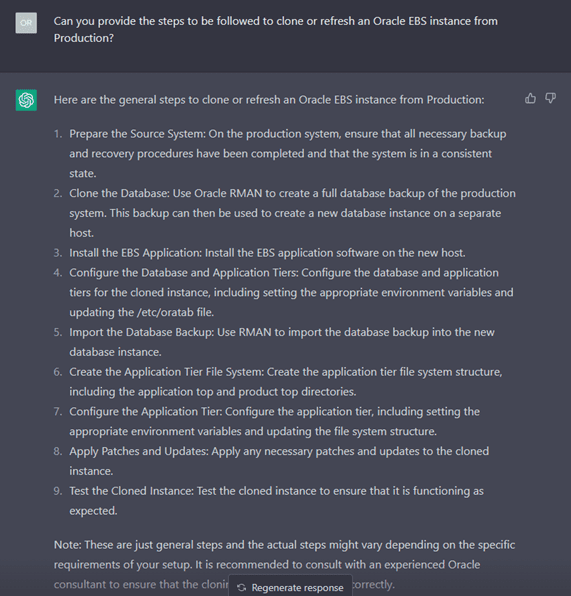
The responses generated are generic but provide enough direction to take necessary action. Furthermore, these responses will only improve with reinforcement learning assisted with human feedback. Below are some examples of responses generated from ChatGPT based on questions asked.
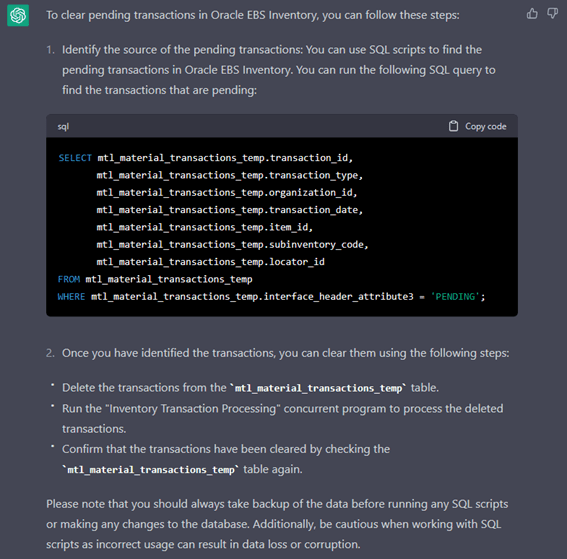
However, it’s worth noting that ChatGPT is a general-purpose language model and may not have the specific expertise of a human Oracle DBA in all cases.
What are some of the limitations of ChatGPT:
Although ChatGPT is a powerful AI-based chatbot, it does have some limitations. It can only provide answers based on the data it has been trained on. ChatGPT is not a search engine, therefore it does not have the ability to search the internet for information. Rather, it uses the information it learned from training data to generate responses. This leaves room for error — so all output should be fact-checked for accuracy and timeliness. As with all AI tools, all business leaders should be aware of the dangers of potential bias. If the data provided is biased, the answers the bot provides will be biased, as well. All companies need to be vigilant about monitoring output from the chatbot to ensure it is free of bias and offensive content. An important limitation is that the quality of the output depends on the quality of the input. A classic example of that is when Google launched Bard, its AI-based chatbot on Feb 9, 2023, whose factual error cost Google a wipeout of 7% of its stock market value.
In other words, expert directions (prompts) generate better answers. As with any technological innovation, there is misuse as well. An example of that is students using ChatGPT for producing college essays and doing their homework. And then there are examples of large language models like GPTZero that uses ChatGPT against itself by analyzing the text for recognition of patterns and counter AI plagiarism.
Conclusion:
Large language models (LLM) have sparked wide interest in the capabilities of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The fact that all major software companies are heavily investing in it shows that there is immense potential in this area and they can revolutionize the way we do work, communicate, process information, and live.
References:
- https://www.searchenginejournal.com/what-is-chatgpt/473664/
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/bernardmarr/2022/12/21/chatgpt-everything-you-really-need-to-know-in-simple-terms/?sh=37ba3007cbca
- https://www.npr.org/sections/money/2023/01/17/1149206188/this-22-year-old-is-trying-to-save-us-from-chatgpt-before-it-changes-writing-for
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to harness the power of AI in your database management.
Whether you have questions about this blog or are looking for ways to enhance your Oracle databases with ChatGPT, contact the author or our expert team of DBAs to learn more.
Nitin Jain – Principal Consultant
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/njain82/